Navigating the Complexities of Healthcare: Hospital Management System Development
- TECHVIFY Team
- 0 Comments
Hospitals today are more than just buildings where people go to heal; they are complex organizations that face an array of challenges. Inefficiencies, bureaucratic red tape, and outdated management practices have led to high costs and overworked staff, making it tough for hospitals to provide the best care. To keep a hospital running smoothly, it’s clear that a top-notch team and streamlined management are essential. That’s where a Hospital Management System (HMS) comes in. An effective HMS doesn’t just tackle the challenges head-on—it also supports doctors, empowers staff, and speeds up paperwork, all while ensuring that everyone can focus more on patient care and less on the tedious tasks.
In this article, TECHVIFY‘s experts are going to unfold the steps of Hospital Management System Development, giving you the know-how to create a system that can transform the way a hospital operates, making it more efficient and effective.
Interesting Facts & Figures:
- According to SpringerLink research, hospitals that have integrated HMS faced a 19% to 20% reduction in workload.
- According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global healthcare IT market is expected to reach $821.1 billion by 2026 from $326.1 billion in 2021, at a CAGR of 20.3% during the forecast period.
- The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine services, which have become a standard component of HMS offerings.
1. What is a Hospital Management System (HMS)?
In the complex ecosystem of healthcare, a hospital management system (HMS) serves as a digital lifeline, a web or cloud-based software that integrates data from all departments and automates the hospital process. Just as pilots need a control panel to fly planes safely, hospitals need HMS to navigate the complexities of healthcare delivery effectively.
At its core, an HMS helps coordinate the efforts of hospital staff, enabling clear communication with doctors and efficient assignment of duties. Since hospital personnel handle sensitive patient data — where accuracy and confidentiality are paramount — even a minor error can lead to significant consequences, including financial losses that can escalate to staggering amounts.
The security of patient data is a paramount concern in healthcare, making an advanced HMS not just a preference but a necessity. With threats to data security growing more sophisticated, only a robust HMS can offer the fortress-like protection needed to safeguard clients’ information. It’s not just about preventing breaches that could cost millions; it’s about maintaining the trust that is the foundation of the patient-caregiver relationship.
Implementing an HMS is more than an upgrade to hospital operations — it’s a strategic move to ensure data integrity, streamline processes, and deliver patient care that’s both efficient and secure.
Have a Project Idea in Mind?
Get in touch with experts for a free consultation. We’ll help you decide on next steps, explain how the development process is organized, and provide you with a free project estimate.
2. Types of Hospital Management System Software
A Hospital Management System (HMS) is a vital cog in the healthcare machinery, streamlining routine tasks and securely housing essential data needed for efficient hospital operations. This powerful tool integrates various facets of hospital management, simplifying the collection, storage, and access to information. From patient records to supply chain details, the HMS serves as a centralized platform for hospital staff, providing a multifunctional digital assistant to manage daily responsibilities with ease and precision.
HMS software comes in various forms, each tailored to the specific needs of a healthcare facility. The complexity, functionality, and scale of an HMS can vary, influenced by factors such as the size of the medical establishment, its particular requirements, and available budget. Broadly, HMS software can be categorized into the following types:
- Operational and Tactical: Tailored to optimize the day-to-day operations and strategic planning within a hospital.
- Patient Administrative: Enhances patient engagement and administrative processes, from registration to discharge.
- Subject-based: Concentrates on the management of electronic patient health records, such as EMRs and EHRs.
- Task-Based: Allocates and tracks staff responsibilities and duties, supporting daily operational tasks.
- Billing System: Oversees financial transactions, from patient billing to insurance claims, ensuring fiscal health.
- Clinical Decision Support: Integrates with diagnostic tools and medical databases to assist healthcare providers in making informed treatment decisions.
- Inventory Management: Monitors and controls the stock of medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and equipment, ensuring optimal inventory levels.
- Appointment Scheduling: Streamlines the process of scheduling patient appointments, reducing wait times and improving service delivery.
- Compliance Management: Ensures that hospital practices adhere to the latest healthcare regulations and standards, simplifying the compliance process and reducing risk.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides powerful data analysis tools to generate detailed reports, helping administrators make informed decisions based on real-time data and trends.
Each type of HMS can operate independently or be part of a comprehensive system that combines multiple functionalities tailored to the institution’s requirements. The aim is to create a synergistic environment where technology enhances workflow efficiency, data integrity, and patient satisfaction in the hospital setting.
3. Key Stakeholders in Hospital Management System Utilization
The effectiveness of a Hospital Management System (HMS) hinges on its ability to cater to the diverse needs of its users. From administrative staff managing the day-to-day operations to medical professionals providing care and patients seeking services, each group interacts with the HMS in unique ways.
Understanding these interactions is crucial for developers, as it guides the design and functionality of the HMS to ensure it is intuitive, compliant, and efficient for all users. Here’s a closer look at the primary users of an HMS:
3.1 Hospital Administration
The administrative team, which encompasses roles in finance, human resources, and accounting, relies on the HMS for streamlined access to a patient’s non-clinical data. They require functionalities that allow them to manage hospital operations effectively while safeguarding patient confidentiality and meeting regulatory standards.
3.2 Medical Professionals
Medical staff, including doctors, nurses, and lab technicians, represent the core users of the HMS. They need advanced features to access comprehensive medical records, facilitate accurate diagnoses, and plan treatments. The system must present critical information in a clear and accessible manner to support the delivery of high-quality patient care.
3.3 Patients
Patients typically interact with the HMS for making appointments, obtaining test results, and tracking their health records. An HMS with a patient-friendly interface enhances their healthcare experience by simplifying communication and providing convenient access to their personal health information, which is especially important in the era of telemedicine.
4. Advantages of Implementing a Hospital Management System
The adoption of a Hospital Management System (HMS) offers a transformative potential for healthcare facilities, streamlining their processes and significantly boosting the efficiency of their staff members. Here are the expansive benefits of implementing a sophisticated HMS:
4.1. Speeding Up Operational Processes
An HMS revolutionizes the way hospitals operate by automating daily tasks and optimizing the overall user experience. This leads to an enhanced flow of information between patients and healthcare providers. With functionalities that allow for online communication, the time taken for patients to receive care is dramatically reduced.
The software enables appointments to be scheduled, information to be exchanged, and services to be delivered with unprecedented speed and efficiency. This aspect of healthcare delivery is further explored in articles such as “How Could Software Improve Healthcare?” where the impact of technology on patient care is discussed in greater detail.
4.2. Digitization of Medical Records
The HMS brings about a digital revolution in medical record-keeping, allowing for the rapid access and secure handling of patient information. This access is critical for healthcare providers who rely on historical data, current test results, and ongoing treatment plans to make informed decisions.
For patients, the ability to book appointments, review test results, and understand their treatment options at any time is empowering and facilitates a more proactive approach to their health. Moreover, the digitization of records minimizes the risk of errors that can occur with manual record-keeping, promoting safer and more reliable patient care.
4.3. Enhancing Communication
Effective communication is the backbone of any successful healthcare operation. An HMS serves as a comprehensive platform, connecting different departments, facilitating the seamless exchange of information, and ensuring that critical data such as test results and medication orders are communicated without delay.
This interconnectedness is pivotal for the swift diagnosis and treatment of patients, and it fosters an environment of collaboration and teamwork among hospital staff. The HMS eliminates the silos that can often slow down the treatment process, ensuring that doctors have all the information they need at their fingertips.
4.4. Resource Management Optimization
Resource management is a complex task in any hospital setting, but an HMS can dramatically simplify this challenge. By efficiently managing a hospital’s resources, an HMS can help administrators oversee supply chains, maintain and utilize equipment effectively, and allocate staff where they are most needed.
This comprehensive management capability extends to scheduling, which is often a significant administrative burden, allowing for more efficient use of both human and material resources. The result is a leaner operation that can adapt to the dynamic nature of healthcare demands without sacrificing patient care quality.
4.5. Streamlining Finance and Accounting
Financial management within a hospital is an intricate and critical function that an HMS can significantly enhance. It streamlines the financial workflow by automating billing processes, generating invoices, and facilitating the tracking of payments and expenses.
This financial clarity is not only important for day-to-day operations but also provides valuable insights for long-term strategic planning. With a robust HMS, hospitals can maintain financial health, ensuring that they can continue to invest in quality patient care and new technologies.
Let’s talk
A consultation with the Client Relationship Manager, who represents TECHVIFY, without any commitment from your side, will give you:
- Structured and clear vision of your future application
- Information about how our software development company guarantees 100% on-time and on-budget delivery
- Recommendations for choosing the tech stack
- Advice on further steps
- Business-side recommendations
- Rough project estimation on software development
TECHVIFY is right where you need. Contact us now for further consultation:
4.6. Informing Marketing Strategies
The wealth of data generated and stored within an HMS is a goldmine for informing marketing strategies. Hospital administrators and marketing teams can analyze trends, patient feedback, and service usage to develop targeted campaigns and outreach programs.
This can lead to improved patient engagement, higher satisfaction, and ultimately, a stronger reputation in the competitive healthcare market. By leveraging the data from an HMS, hospitals can craft personalized communication and services that resonate with their patient population.
4.7. Simplifying Insurance Claims Processing
Dealing with insurance claims can be a cumbersome and confusing process for patients and hospital staff alike. An HMS simplifies this process by integrating insurance workflows directly into the system, making it easier for patients to submit claims and for hospitals to manage them.
4.8. Time Conservation
The automation of administrative tasks that an HMS provides is a significant time-saver. By reducing the need for manual entry and record-keeping, healthcare providers can dedicate more time to patient care. This shift away from paperwork also reduces the likelihood of clerical errors and improves the overall efficiency of the hospital’s operations.
In an industry where time is of the essence, the time savings afforded by an HMS can make a substantial difference in patient outcomes.
4.9. Empowering Patients with Self-Service Options
In today’s digital age, patients expect to have more control and accessibility when it comes to their healthcare. An HMS meets these expectations by allowing patients to engage with their healthcare providers through self-service portals.
These portals enable patients to schedule their own appointments, access test results, and review their medical records at their convenience, fostering a sense of autonomy and involvement in their healthcare journey.
4.10. Elevating Customer Experience
The HMS extends beyond operational benefits to enhance the overall customer experience. By integrating 24/7 assistance, such as live chat or call center services, patients can access support whenever they need it. Online consultations, telemedicine capabilities, and electronic payment systems offer unparalleled convenience in a Hospital Management System.
5. Basic Requirements for Hospital Management System Development
When embarking on the development of a Hospital Management System (HMS), it’s crucial to incorporate features that cater to the diverse needs of its users—hospital staff, patients, and third-party service providers. Below, we outline the foundational requirements that should be meticulously considered to ensure the system is user-friendly, secure, and efficient:
5.1. User-Friendly Interface
- Intuitive Navigation: Ensure the HMS has a clear, logical layout that guides users through their tasks without confusion, suitable for all skill levels.
- Accessible Design: The interface should follow best practices for accessibility, allowing users with disabilities to interact with the system effectively.
5.2. Data Compliance and Security
- Rigorous Protection: Implement strong encryption and security protocols to protect sensitive data against unauthorized access and breaches.
- Regulatory Adherence: The HMS must be designed to meet the requirements of GDPR, HIPAA, and other relevant healthcare regulations to ensure compliance and avoid legal penalties.
5.3. Robust Data Management
- Diverse Data Handling: Develop the system to accommodate various data types, including text, images, and videos, ensuring they are stored and accessed efficiently.
- Policy Framework: Establish clear policies for data collection, access, retention, and disposal to maintain data integrity and patient privacy.
5.4. Rapid Responsiveness
- Quick Access: Design the system to provide immediate access to patient records and hospital data to support fast-paced medical environments.
- Streamlined Processes: Incorporate features that automate and expedite routine tasks such as patient admissions, billing, and inventory management, reducing wait times and increasing efficiency.
6. Must-Have Features for Developling a Hospital Management System
In the rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, the implementation of a comprehensive Hospital Management System (HMS) is pivotal for enhancing patient care and operational efficiency. An HMS serves as the digital backbone of a healthcare institution, integrating various functionalities that span from patient registration to inventory management. Let’s delve into the integral components of an HMS that collectively work to streamline hospital management, improve patient outcomes, and drive the digital revolution in healthcare.
6.1. Patient Registration and Electronic Health Record (EHR)
- Comprehensive Data Entry: The HMS should offer a seamless registration process that captures all essential patient information, serving as the cornerstone for patient interaction.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration: EHRs are critical for consolidating patient data, which includes medical and financial information, improving the quality of care, reducing errors, and facilitating better communication.
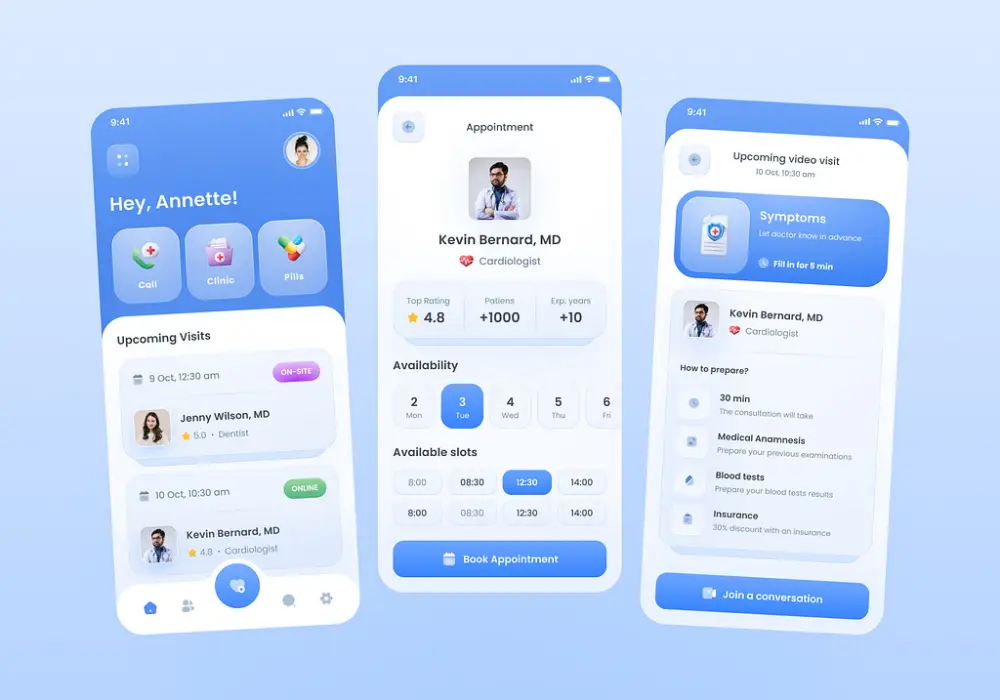
6.2. Booking Appointments
- Flexible Scheduling: The system must enable patients and doctors to schedule and manage appointments with ease, adjusting for changes as required.
- Integrated Notifications: Automated notifications via SMS or email should confirm bookings and inform of any changes, optimizing the appointment management process.
6.3. Billing and Accounting Management
- Automated Billing: The HMS should have a comprehensive billing module that accurately calculates costs and streamlines the financial transactions for treatments and services.
- Financial Analysis: By automating accounting, the system should also provide valuable insights into the hospital’s financial health, enabling strategic financial planning.
6.4. Doctor’s Profile Section
- Detailed Physician Profiles: The system should feature an informative section on each physician, including qualifications, availability, and services offered, to aid patients in making informed decisions.
- Availability and Scheduling: A real-time schedule of doctors’ availability should be maintained within the HMS for efficient appointment setting and to enhance transparency for patients.
6.5. Laboratory Management
- Efficient Test Result Management: The HMS should facilitate quick access to lab results, notifying both doctors and patients promptly, which is crucial for timely diagnoses and treatment.
- Centralized Lab Information: All laboratory information should be accessible in one place within the HMS to streamline the process of ordering and reviewing tests.
6.6. Inventory Management
- Supply Tracking: The HMS must have a robust inventory management system that monitors medical supplies and predicts the need for restocking to prevent shortages.
- Expiration Monitoring: The system should also manage the inventory to track expiration dates of drugs, ensuring patient safety and compliance with regulations.
6.7. Statistical Data and Forecasting
- Data-Driven Decisions: The HMS should be capable of generating statistical reports on finances, patient demographics, staff performance, and inventory to inform the hospital’s strategic planning.
- Easy Reporting: A feature that allows easy creation of comprehensive reports with just a few clicks is essential for monitoring and improving hospital operations.
6.8. Customer Support
- Reliable Helpdesk: Considering the complexity and critical nature of the HMS, a dedicated support desk is crucial for resolving any software issues and maintaining continuous hospital operations.
6.9. Telemedicine Solutions
- Virtual Consultations: The HMS should include a telemedicine feature that enables patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely, expanding the reach of medical services.
- Teleconferencing Capabilities: Integration with teleconferencing tools is essential to provide remote healthcare services effectively and securely.
6.10. Mobile App for Patients and Staff
- Patient Engagement: A mobile app should provide patients with access to their treatment schedules, appointment details, lab results, and bill payments.
- Staff Coordination: The app should also facilitate efficient communication and coordination among hospital staff, allowing doctors to stay informed and connected even when off-site.
TECHVIFY – Global AI & Software Solution Company
From Startups to Industry Leaders: TECHVIFY prioritizes results, not just deliverables. Accelerate your time to market and see ROI early with high-performing teams, AI (including GenAI) Software Solutions, and ODC (Offshore Development Center) services.
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: (+84)24.77762.666